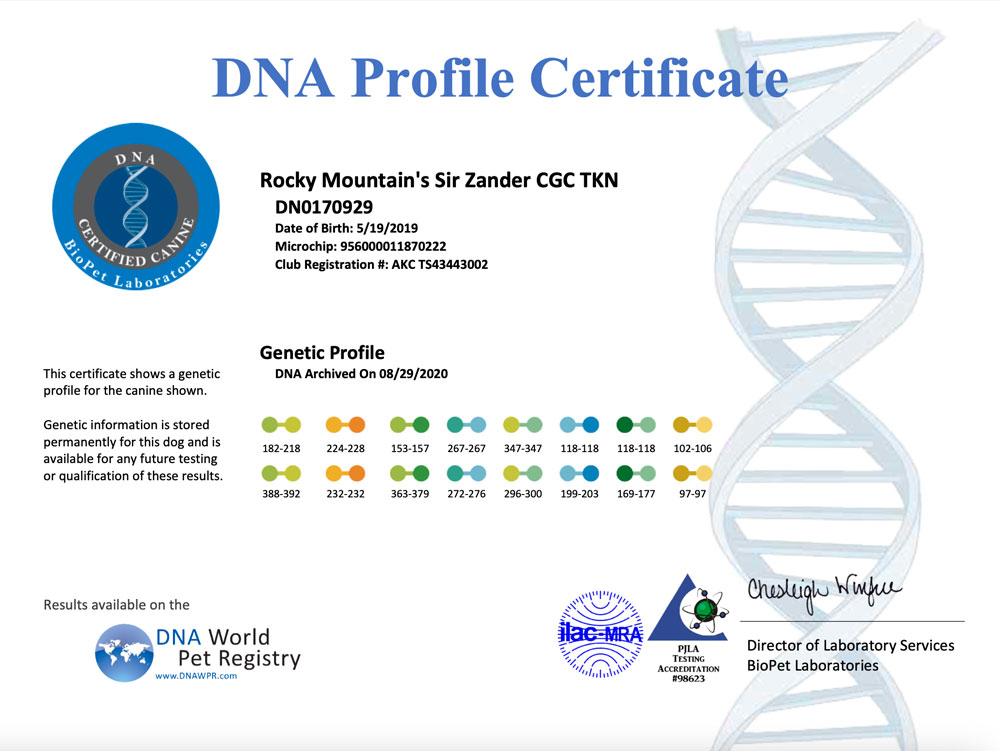
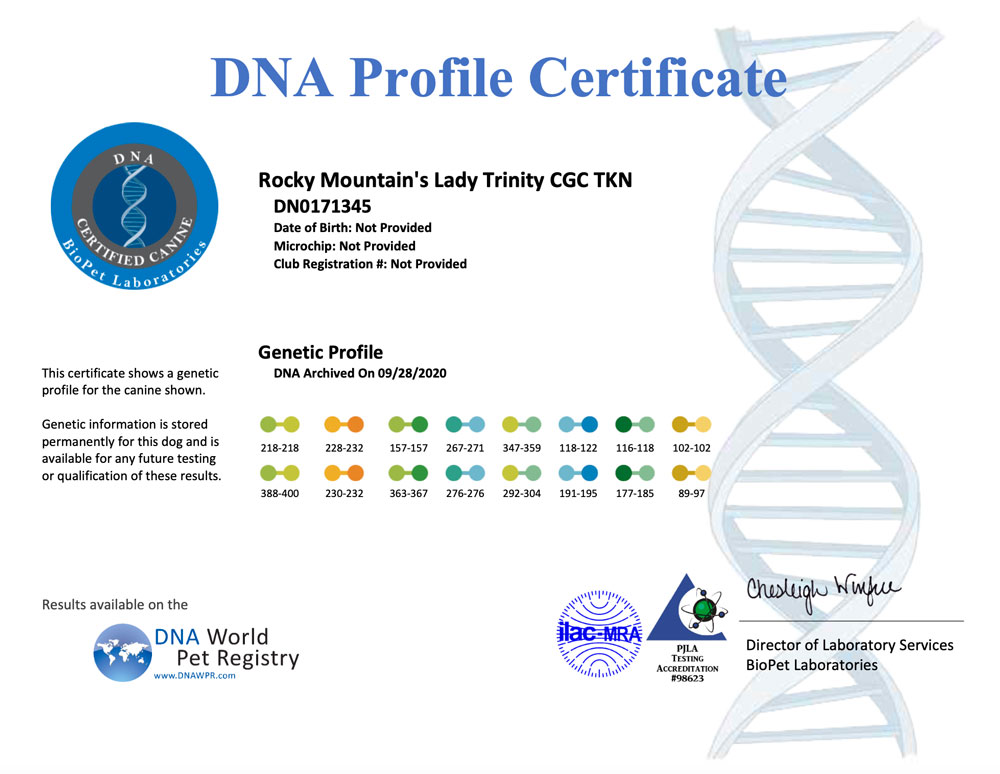
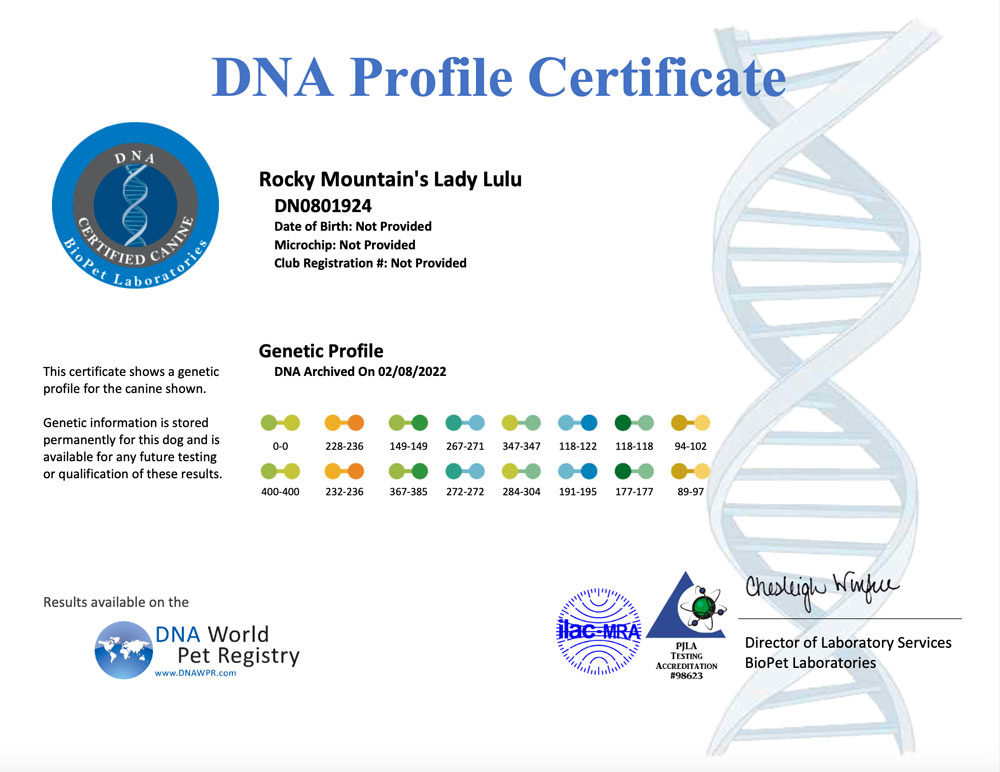
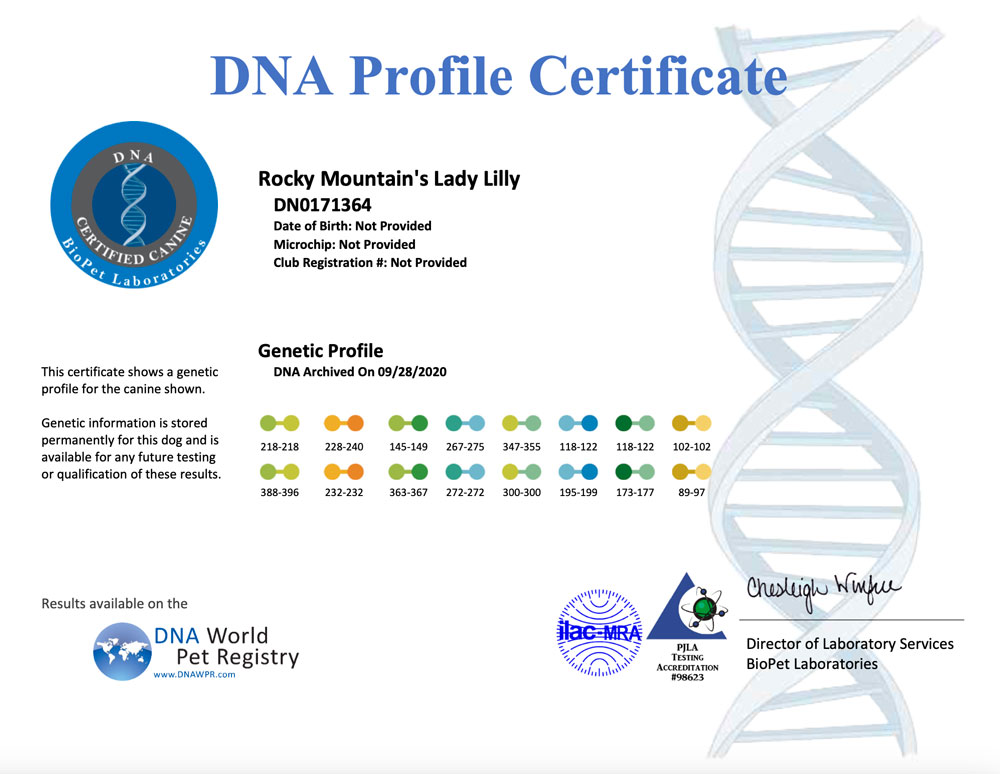
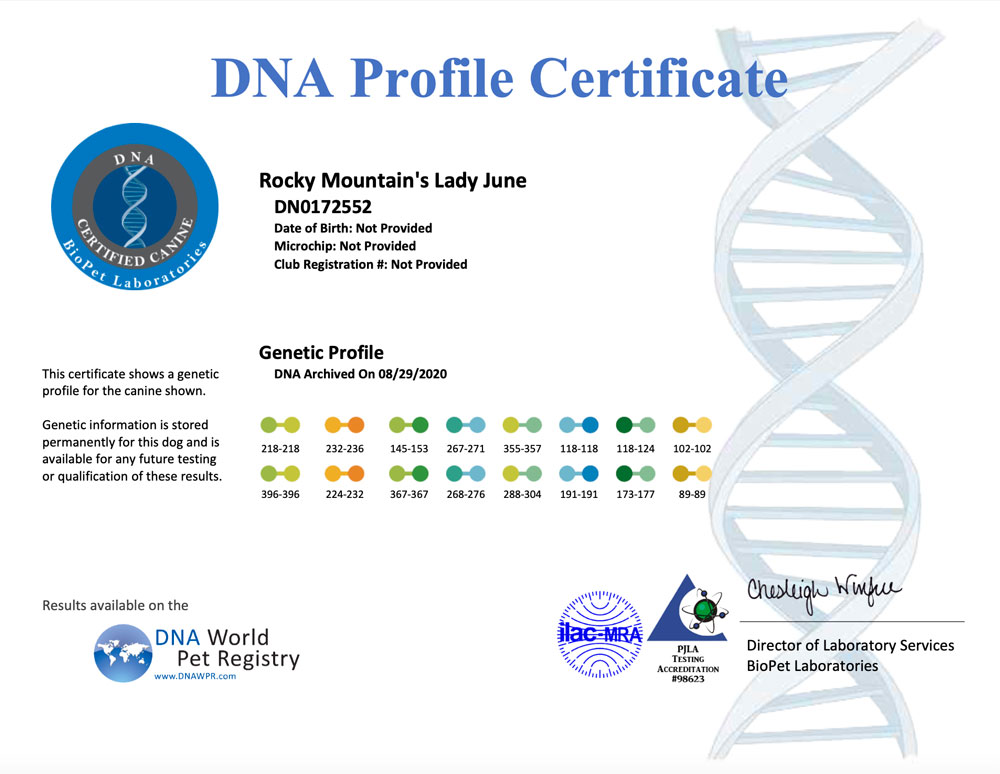
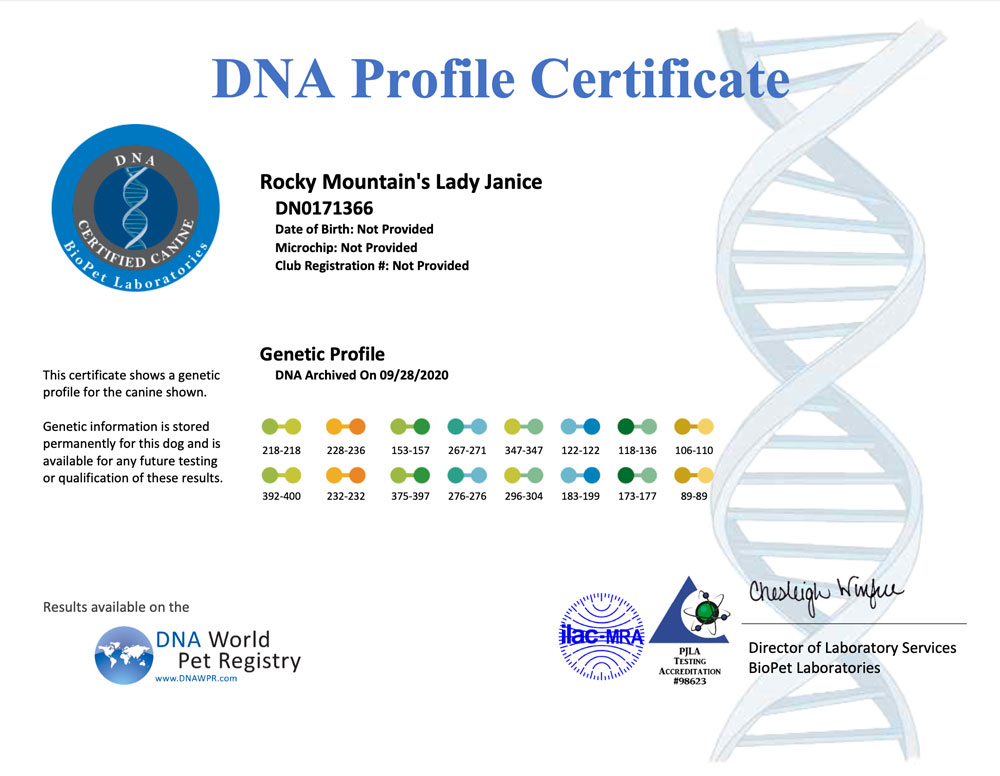
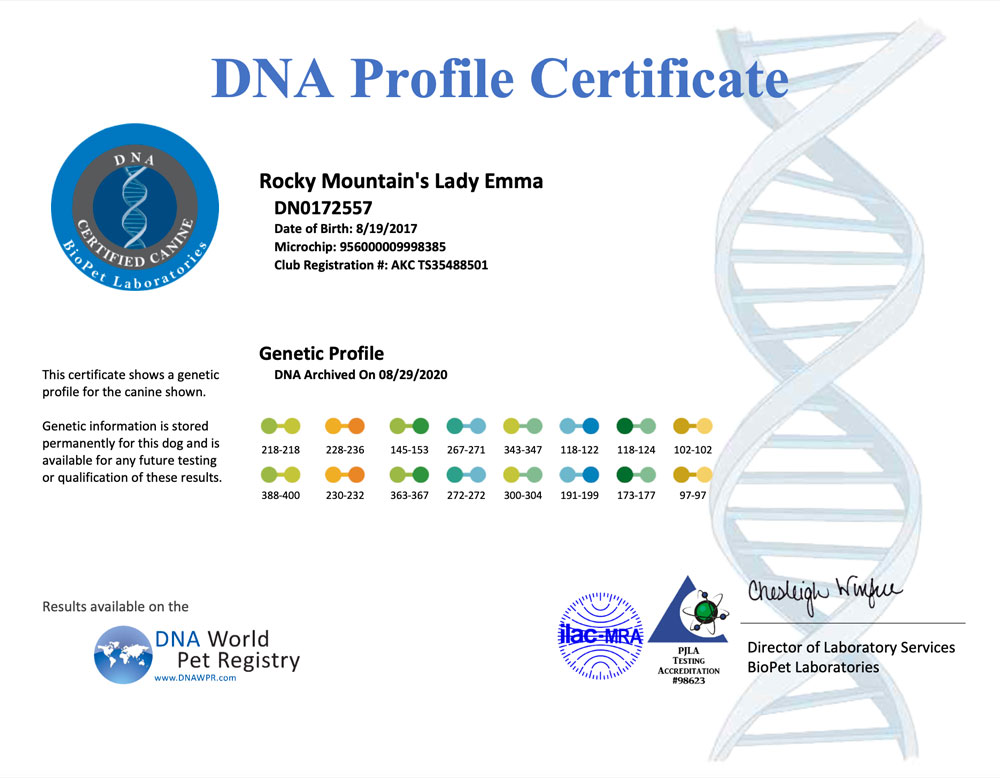
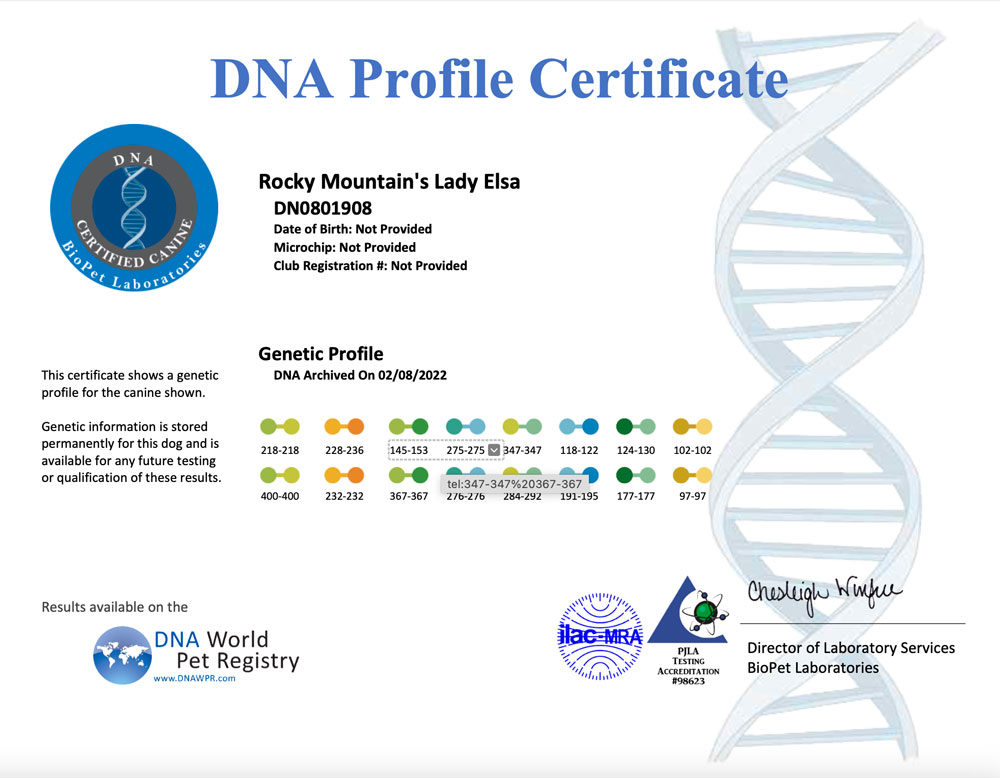
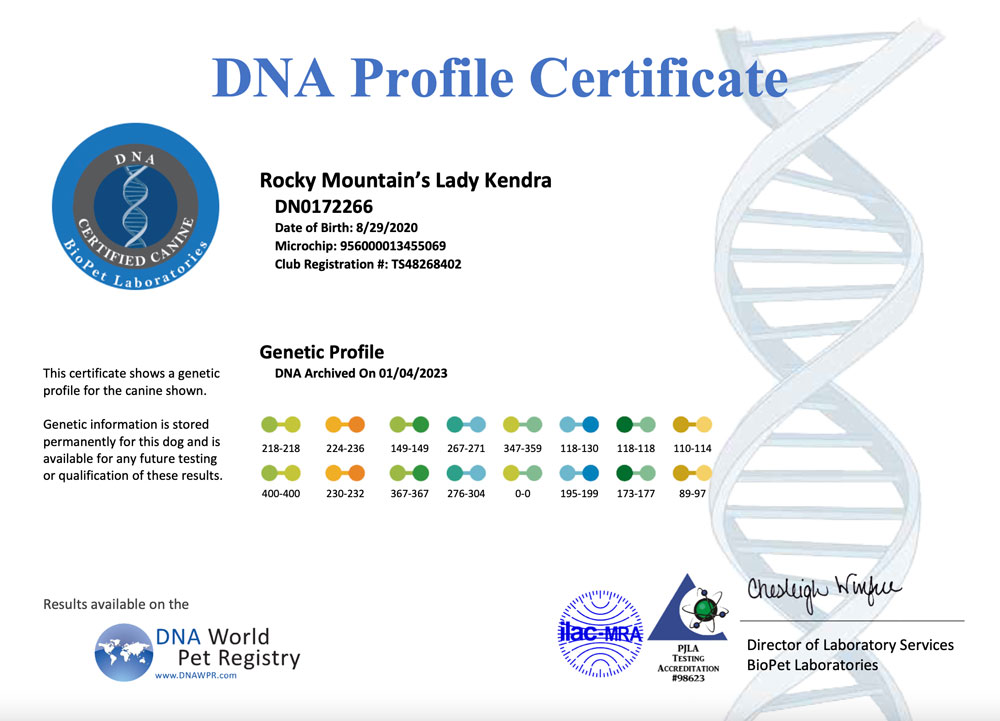
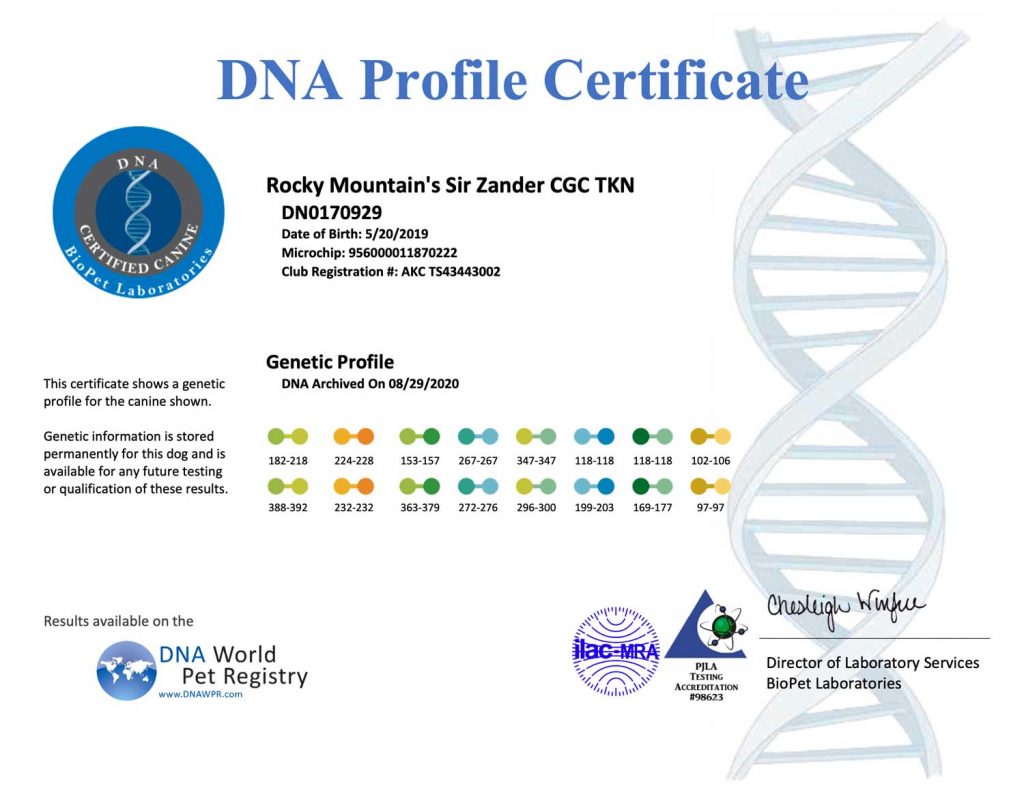
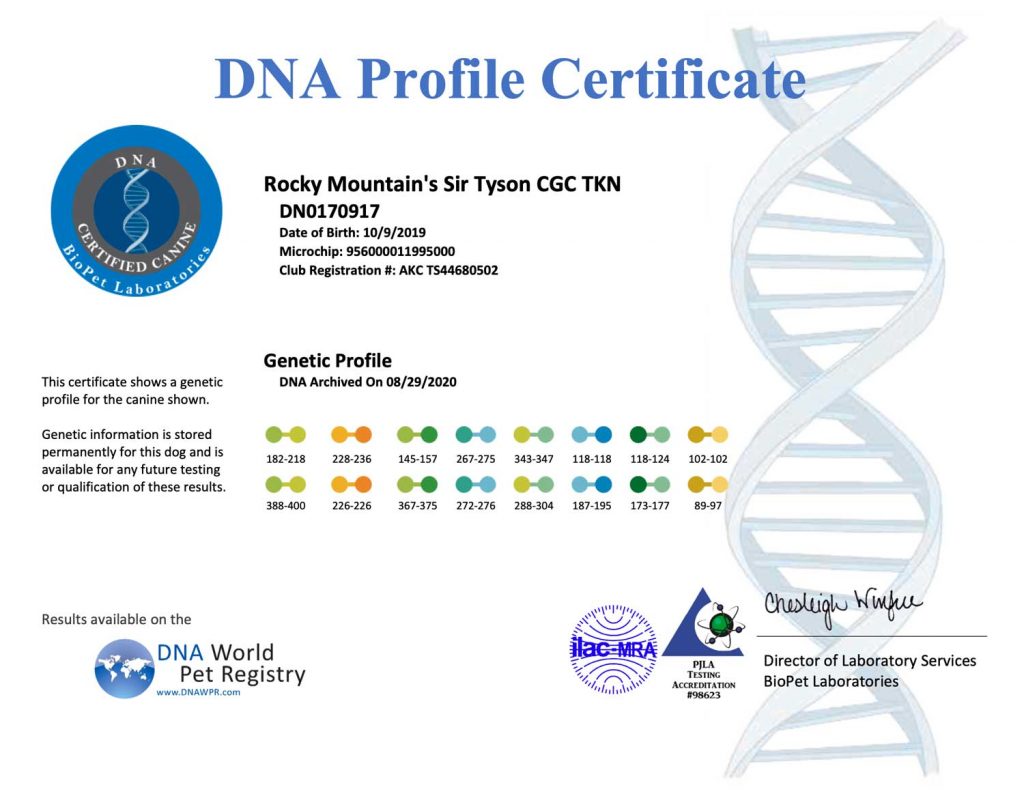
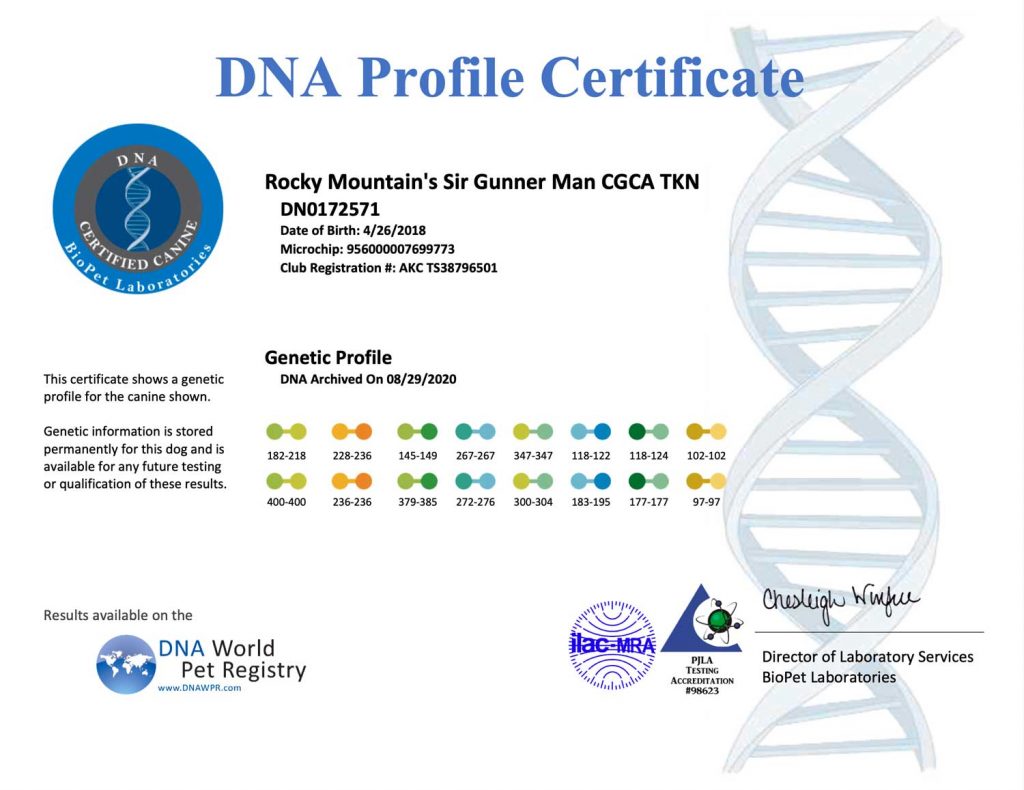
A DNA profile for a dog is a unique set of genetic markers that can be used to identify and differentiate individual dogs. DNA profiling involves analyzing specific regions of a dog’s DNA to create a unique genetic fingerprint. The resulting DNA profile can be used for a variety of purposes, including:
- Identification: DNA profiling can be used to identify individual dogs, even if they do not have any visible or readable identification tags or microchips. This can be particularly useful in cases where a dog is lost or stolen.
- Parentage testing: A DNA profile can be used to determine the parentage of a dog. This can help to ensure the accuracy of breeding records and prevent inbreeding.
- Breed identification: DNA profiling can be used to determine the breed or breeds that a dog belongs to. This can be useful for owners who want to learn more about their dog’s ancestry, as well as for breeders who want to ensure the accuracy of their breeding programs.
- Health screening: A DNA profile can also be used to screen for genetic diseases and health risks. Certain genetic markers have been associated with an increased risk of specific diseases, and DNA profiling can help to identify dogs that may be at higher risk.
Overall, DNA profiling is a powerful tool that can be used for a variety of purposes in dog breeding and ownership communities. It can help to improve breeding practices, prevent health issues, and ensure the accuracy of identification and pedigree records.
How is a DNA Profile for dogs done?
DOG DNA profiling is typically done using a simple and non-invasive cheek swab to collect a DNA sample from the dog. Here are the general steps involved in dog DNA profiling:
- DNA sample collection: A swab is used to collect cells from the inside of the dog’s cheek. The swab is rubbed gently against the inside of the cheek to collect cells, which contain DNA.
- DNA extraction: The cells collected on the swab are processed to extract the DNA. This involves breaking open the cells and isolating the DNA.
- DNA analysis: The extracted DNA is analyzed using a technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR). PCR amplifies specific regions of the DNA that contain genetic markers used for profiling.
- Genetic marker analysis: The amplified DNA is then analyzed to determine the unique set of genetic markers for the dog. These markers are used to create the dog’s DNA profile.
- Database comparison: The DNA profile is then compared to a database of known dog DNA profiles to identify matches or determine the breed or breeds that the dog belongs to.
The results of the DNA profiling can be used for a variety of purposes, including parentage testing, breed identification, and health screening. DNA profiling is a reliable and accurate method of identifying and differentiating individual dogs and can provide valuable information for breeders, owners, and veterinarians.